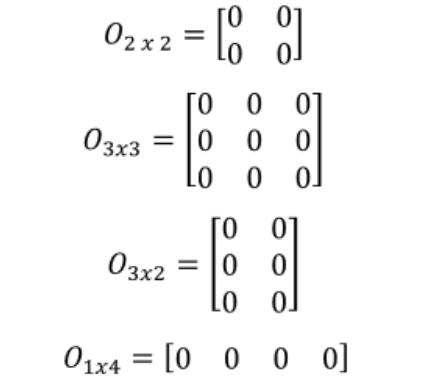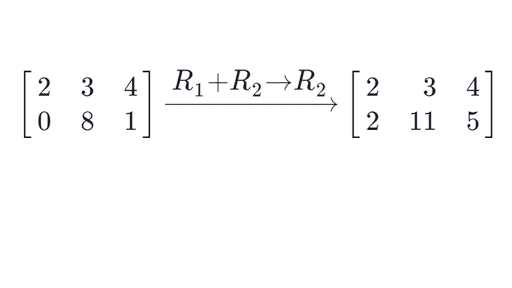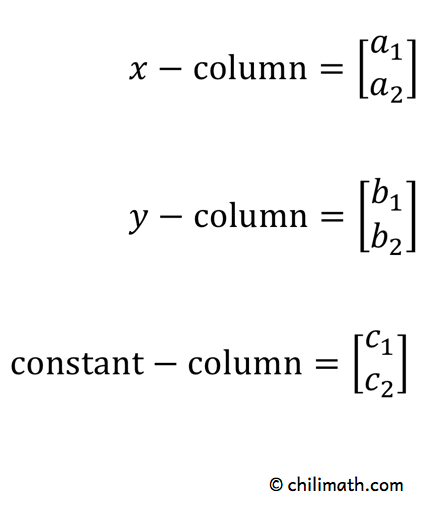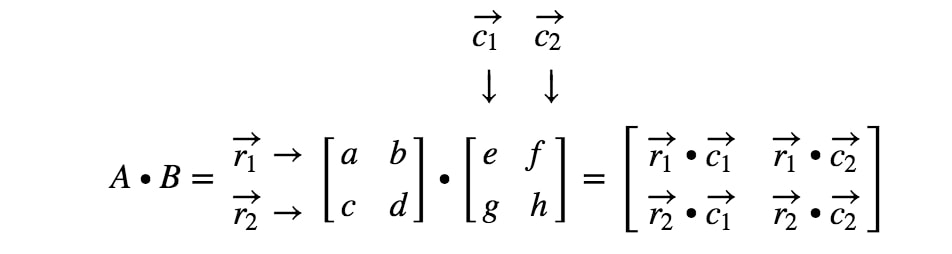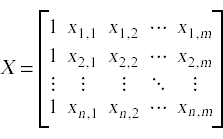2 X 1 Column Matrix

A matrix is a rectangular arrangement or array of numbers often called elements.
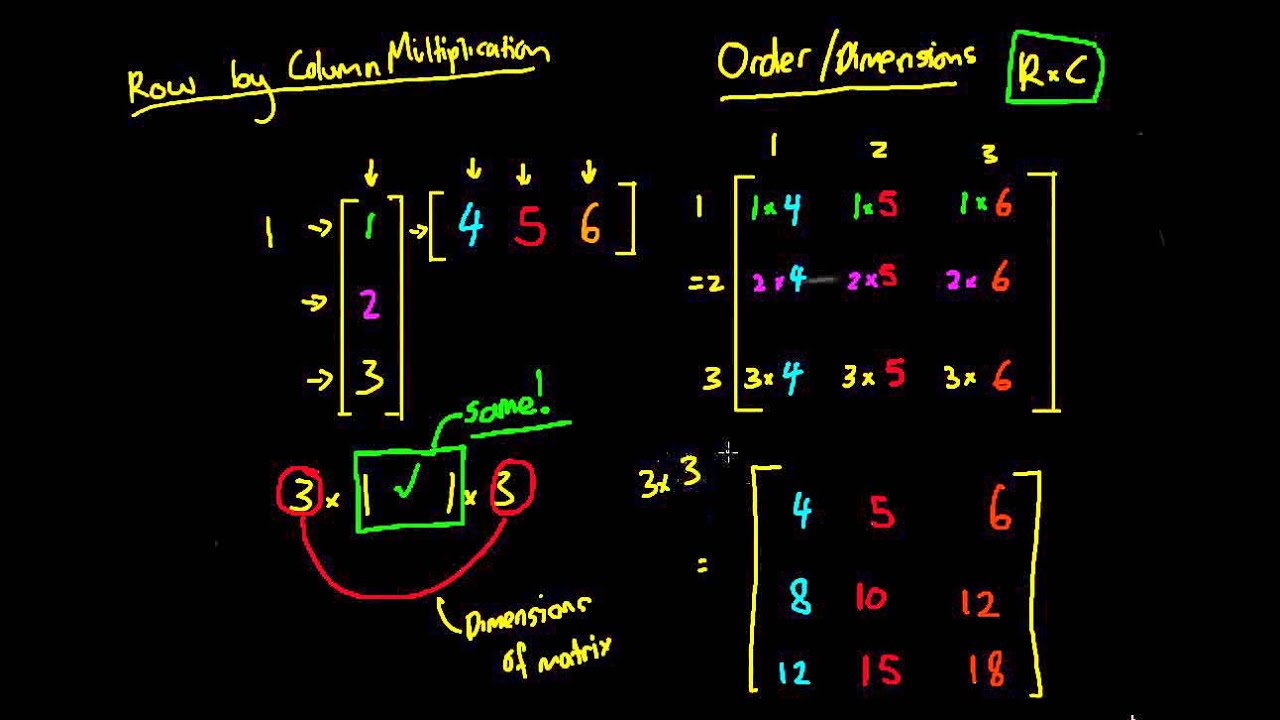
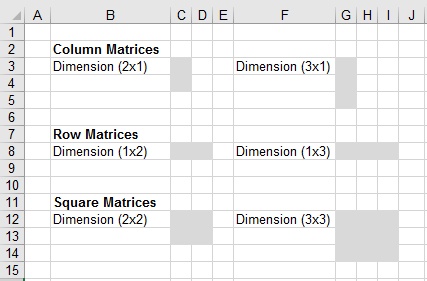
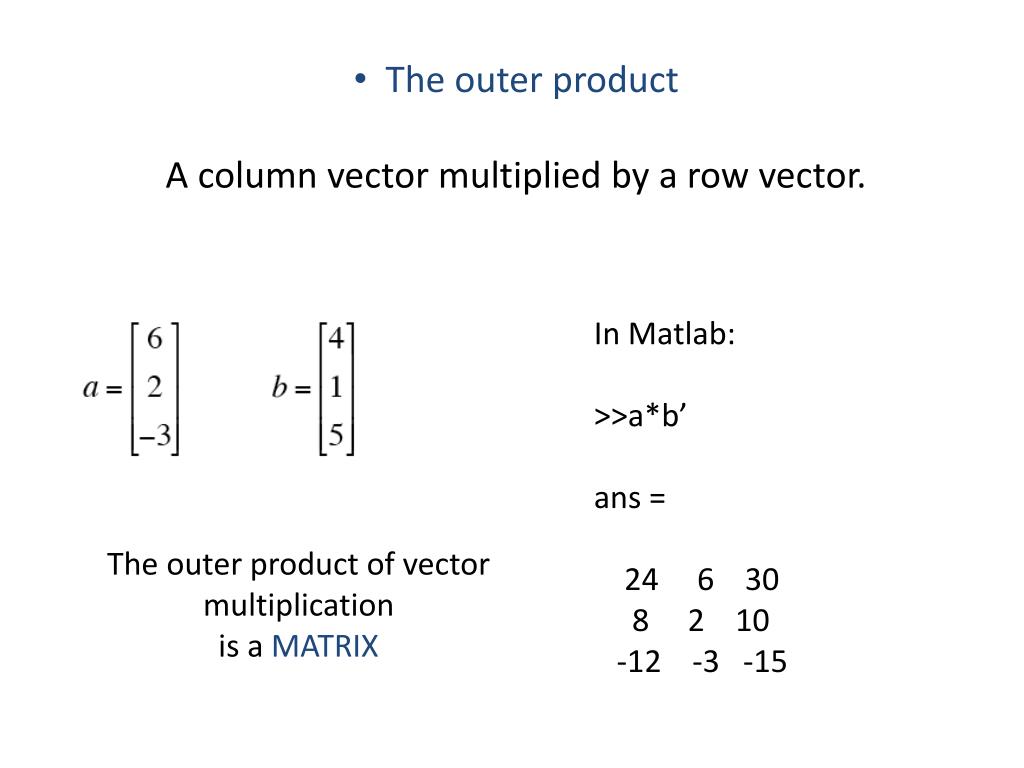
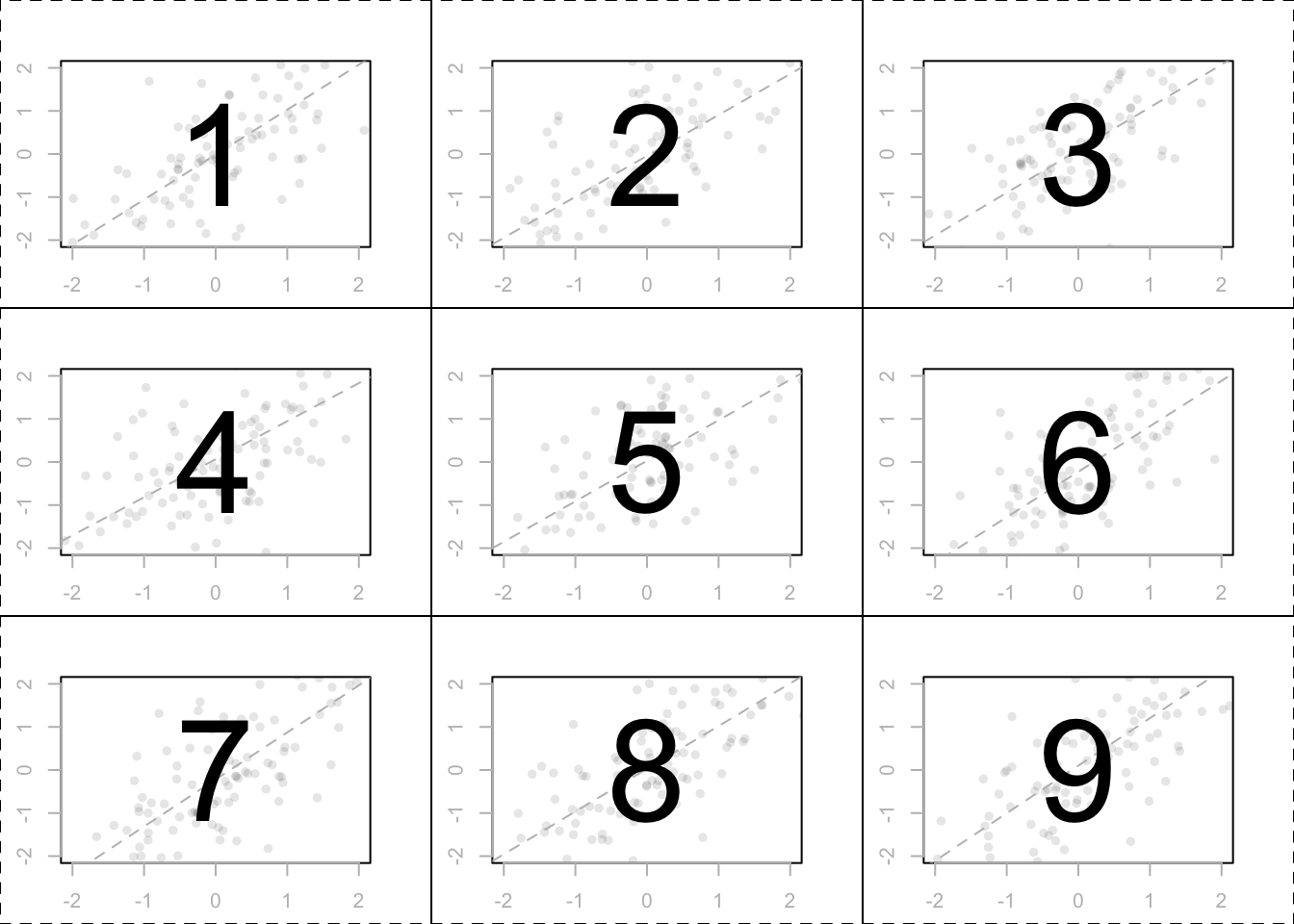
2 x 1 column matrix. Provided that they have the same size each matrix has the same number of rows and the same. For example the dimension of the matrix below is 2 3 read two by three because there are two rows and three columns. In linear algebra a column vector or column matrix is an m 1 matrix that is a matrix consisting of a single column of m elements. That is c is a 2 5 matrix.
A 1 1 b 1 1 a 1 2 b 2 1 a 1 3 b 3 1 c 1 1. In mathematics a matrix plural matrices is a rectangular array or table see irregular matrix of numbers symbols or expressions arranged in rows and columns. Throughout boldface is used for the row and column vectors. In general the i j entry of a matrix a is written a ij and the statement.
The resulting matrix xβ has n rows and 1 column. A 2 4 1 2 ans 5 11 9 7 4 14. A matrix this one has 2 rows and 3 columns to multiply a matrix by a single number is easy. For example since the entry 2 in the matrix above is in row 2 column 1 it is the 2 1 entry.
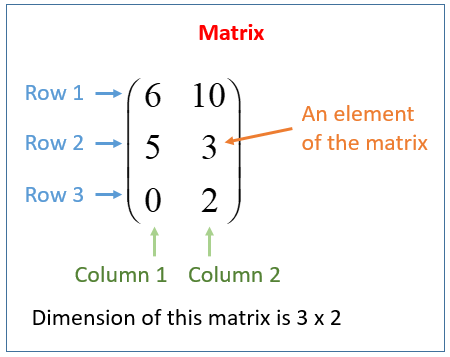
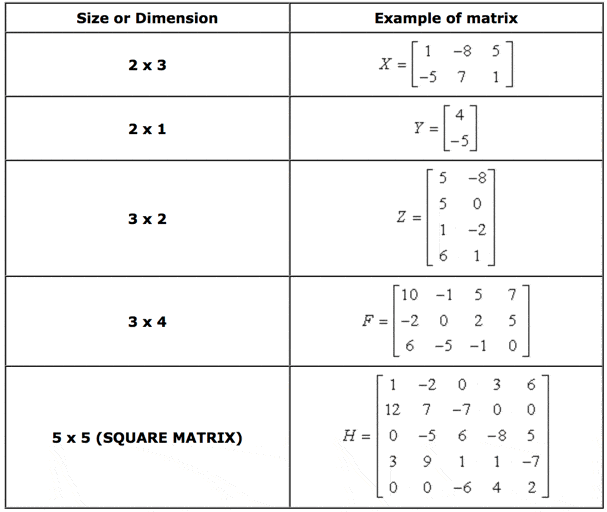
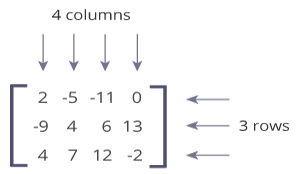
The size or dimensions m n of a matrix identifies how many rows and columns a specific matrix has. Similarly a row vector or row matrix is a 1 m matrix that is a matrix consisting of a single row of m elements. The resulting matrix c ab has 2 rows and 5 columns. The number of rows is m and the number of columns is n.
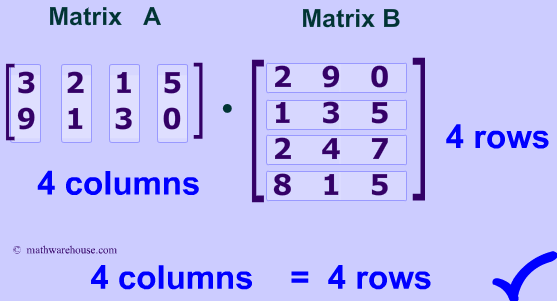
Note that the matrix multiplication ba is not possible. A 2 4 extract the element in row 2 column 4 ans 8 more generally one or both of the row and column subscripts can be vectors. Let us define the multiplication between a matrix a and a vector x in which the number of columns in a equals the number of rows in x. So if a is an m n matrix then the product a x is defined for n 1 column vectors x.
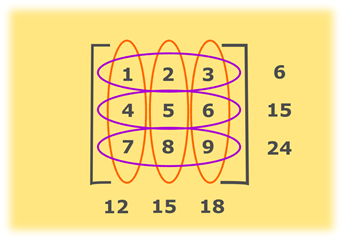
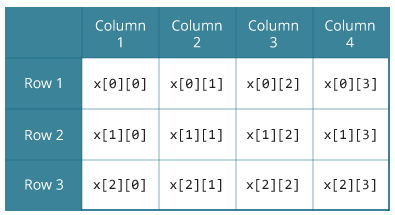
The dimension of a matrix must be known to identify a specific element in the matrix. Multiplying a matrix by another matrix. We call the number 2 in this case a scalar so this is called scalar multiplication. Indicates that a is the m x n matrix whose i j entry is a ij.
The 1 2 entry is 0 the 2 3 entry is 1 and so forth. The transpose indicated by t of a row vector is a column vector. These are the calculations.