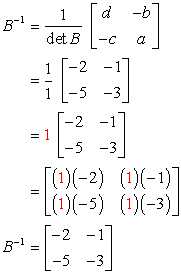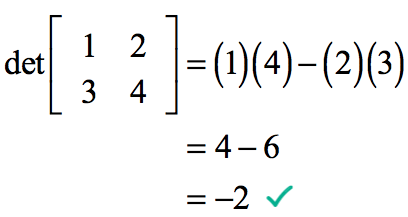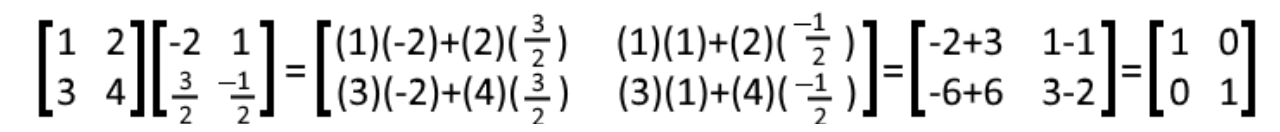1 Cross 2 Matrix

Matrices determinant of a 2 2 matrix inverse of a 3 3 matrix.
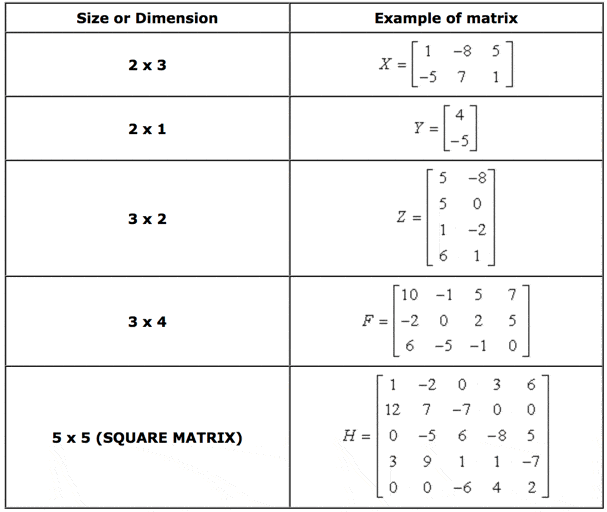
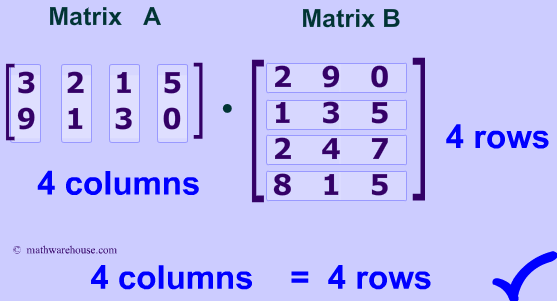
1 cross 2 matrix. Swap the elements of the leading diagonal. The cross product of two vectors a a 1 a 2 a 3 and b b 1 b 2 b 3 is given by although this may seem like a strange definition its useful properties will soon become evident. Just to provide you with the general idea two matrices are inverses of each other if their product is the identity matrix. For example the dimension of the matrix below is 2 3 read two by three because there are two rows and three columns.
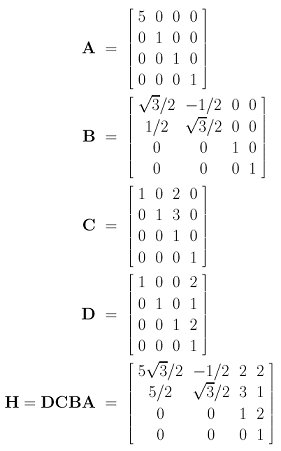
Inverse of a 2 2 matrix. In physics the notation a b is sometimes used though this is avoided in mathematics to avoid confusion with the exterior product. Its symbol is the capital letter i. The identity matrix is the matrix equivalent of the number 1.
The leading diagonal is from top left to bottom. There is an easy way to remember the formula for the cross product by using the properties of determinants. The cross product of two vectors a and b is defined only in three dimensional space and is denoted by a b. It is square has same number of rows as columns it can be large or small 2 2 100 100.
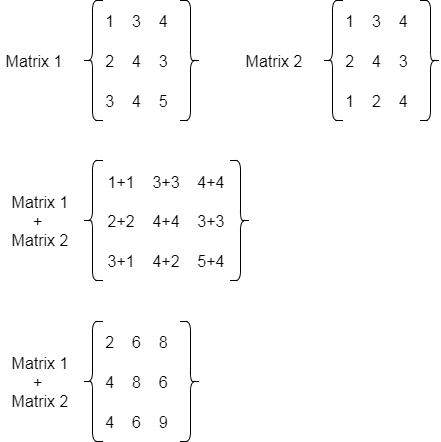
Whatever it has 1s on the main diagonal and 0s everywhere else. In mathematics a matrix plural matrices is a rectangular array or table see irregular matrix of numbers symbols or expressions arranged in rows and columns. Provided that they have the same size each matrix has the same number of rows and the same. Let us find the inverse of a matrix by working through the following example.
A 3 3 identity matrix. The cross product a b is defined as a vector c that is perpendicular orthogonal to both a and b with a direction given by the right hand rule.